When it comes to our health, it's crucial to be aware of the potential risks associated with the medications we take. While medications are designed to improve our health and manage conditions, some can have unintended side effects. One of the most severe potential side effects is a heart attack. Understanding the connection between certain medications and heart attacks can help us make informed decisions about our health care.
Heart attacks, medically known as myocardial infarctions, occur when blood flow to the heart muscle is blocked. This blockage can be caused by various factors, including the use of certain medications. While some medications are essential for treating specific conditions, they may also increase the risk of heart attacks, especially in individuals with pre-existing heart conditions. This article will delve into the different types of medications that may cause heart attacks, how they affect the heart, and what can be done to mitigate these risks.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various classes of medications, from pain relievers to psychiatric drugs, that have been linked to an increased risk of heart attacks. We will also discuss the importance of consulting with healthcare providers, understanding medication labels, and recognizing warning signs to ensure that we are taking steps to protect our heart health. Whether you're a patient, caregiver, or healthcare professional, this article aims to provide valuable insights into the complex relationship between medications and heart health.
Table of Contents
- What is a Heart Attack?
- How Do Medications Affect the Heart?
- Medications and Their Impact on Heart Health
- Which Pain Relievers Can Increase Heart Attack Risk?
- Are Anti-inflammatory Drugs Harmful to the Heart?
- The Role of Antidepressants in Heart Attacks
- Can Antibiotics Cause Heart Attacks?
- Medications for Chronic Conditions and Heart Risk
- Stimulants and Their Effect on Heart Health
- Are There Safe Alternatives?
- Recognizing Warning Signs
- How to Talk to Your Doctor About Medication Risks?
- Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Heart Attack Risk
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is a Heart Attack?
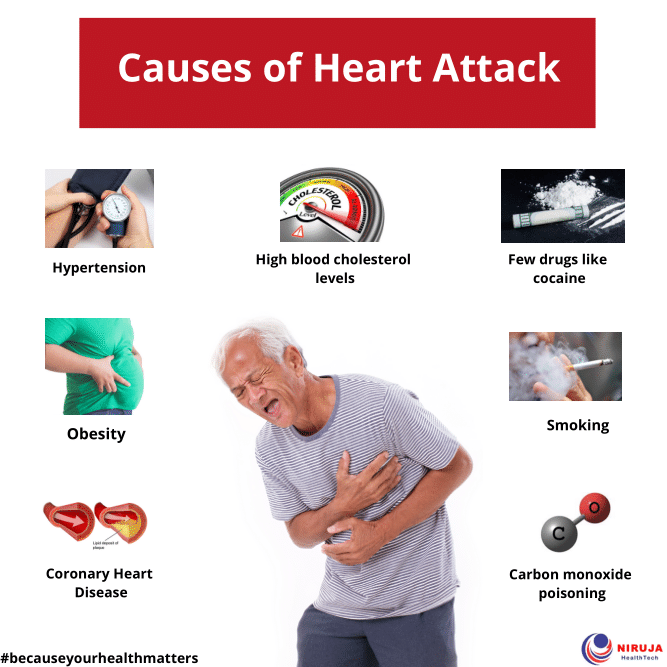
A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, is a serious medical emergency where the supply of blood to the heart is suddenly blocked, usually by a blood clot. The heart muscle requires a constant supply of oxygen-rich blood to function correctly, and when this supply is interrupted, the heart tissue can become damaged. The most common cause of a heart attack is coronary heart disease, where the coronary arteries become narrowed due to a buildup of cholesterol and other substances, known as plaque. Understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and causes of heart attacks is vital in preventing and managing this life-threatening condition.
Symptoms of a Heart Attack
Recognizing the symptoms of a heart attack can save lives. These symptoms may vary between individuals and can be different for men and women. Common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Pain in the arms, neck, jaw, or back
- Shortness of breath
- Cold sweat
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of heart attacks, including:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Stress
- Family history of heart disease
Causes of Heart Attacks
The primary cause of heart attacks is coronary artery disease, which is characterized by the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries due to plaque buildup. Other causes may include severe spasms of the coronary arteries or a tear in the artery wall. It's essential to address these causes through lifestyle changes, medication, or surgical interventions to manage the risk of heart attacks.
How Do Medications Affect the Heart?
Medications can have both beneficial and adverse effects on the heart. While some medications are prescribed to treat heart conditions and reduce the risk of heart attacks, others, even if prescribed for non-cardiac conditions, may inadvertently increase the risk of heart issues. Understanding how medications interact with the cardiovascular system can help individuals and healthcare providers make informed decisions about treatment options.
Cardiovascular System Overview
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. Its primary function is to circulate blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing waste products. Medications can influence this system in various ways, such as altering heart rate, blood pressure, and blood flow, which can either improve or compromise heart health.
Drug Interactions and Heart Health
Medications can interact with each other, leading to increased or decreased effectiveness and potential side effects. Some drug interactions can negatively impact heart health by causing arrhythmias, increased blood pressure, or other cardiovascular issues. It is crucial to consult with healthcare providers about all medications being taken, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to avoid harmful interactions.
Side Effects and Risks
Every medication has potential side effects, some of which can affect the heart. Common cardiovascular side effects include:
- Increased heart rate
- Elevated blood pressure
- Arrhythmias
- Fluid retention
While these side effects may not occur in everyone, individuals with existing heart conditions or risk factors for heart disease should be particularly cautious and monitor their heart health when taking medications.
Medications and Their Impact on Heart Health
Several classes of medications have been linked to an increased risk of heart attacks. While these medications are essential for treating various conditions, it is important to be aware of their potential impact on heart health and take necessary precautions to minimize risks.
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs are commonly used to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and lower fever. However, long-term use or high doses of NSAIDs can increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes. This risk is particularly pronounced in individuals with existing cardiovascular disease or risk factors such as high blood pressure and diabetes.
Antidepressants and Heart Health
Antidepressants are prescribed to manage depression and anxiety disorders. Some antidepressants, particularly certain selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), have been associated with an increased risk of heart attacks. It is important to balance the benefits of treating mental health conditions with the potential cardiovascular risks, especially in individuals with existing heart issues.
Antibiotics and Heart Risk
While antibiotics are essential for treating bacterial infections, some have been linked to cardiovascular side effects, including an increased risk of heart attacks. Fluoroquinolones, a class of antibiotics, have been associated with heart rhythm abnormalities and other cardiovascular concerns. It is crucial to use antibiotics judiciously and under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Which Pain Relievers Can Increase Heart Attack Risk?
Pain relievers, also known as analgesics, are widely used to manage pain and discomfort. However, not all pain relievers are created equal regarding heart health. Some pain relievers, particularly NSAIDs, have been linked to an increased risk of heart attacks.
Commonly Used Pain Relievers
Over-the-counter and prescription pain relievers include:
- Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin)
- Naproxen (Aleve)
- Aspirin
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
Understanding NSAIDs
NSAIDs work by blocking enzymes responsible for inflammation and pain. While effective, they can also affect blood clotting, increase blood pressure, and cause fluid retention, all of which can contribute to an increased risk of heart attacks, especially in individuals with cardiovascular disease.
Safer Alternatives for Pain Relief
For those with heart disease or risk factors, safer alternatives for pain relief include:
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
- Topical pain relievers
- Physical therapy
- Alternative therapies such as acupuncture or massage
Are Anti-inflammatory Drugs Harmful to the Heart?
Anti-inflammatory drugs, including NSAIDs and corticosteroids, are used to reduce inflammation and manage conditions such as arthritis and autoimmune disorders. While these drugs can provide significant relief, they may also pose risks to heart health.
Corticosteroids and Heart Risk
Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are powerful anti-inflammatory medications that can affect the cardiovascular system by increasing blood pressure, causing fluid retention, and altering blood sugar levels. Long-term use of corticosteroids can increase the risk of heart attacks, particularly in individuals with existing heart disease.
Balancing Benefits and Risks
When considering anti-inflammatory drugs, it is important to weigh the benefits of symptom relief against the potential cardiovascular risks. Healthcare providers can help determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment to minimize risks while effectively managing symptoms.
Monitoring Heart Health
Individuals taking anti-inflammatory drugs should monitor their heart health by regularly checking blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and heart rate. Any changes in these parameters should be discussed with a healthcare provider to ensure appropriate management of heart health.
The Role of Antidepressants in Heart Attacks
Antidepressants are a vital component of mental health treatment, helping individuals manage depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders. However, some antidepressants have been linked to an increased risk of heart attacks, particularly in individuals with pre-existing heart conditions.
Types of Antidepressants
Common classes of antidepressants include:
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
- Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
- Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
SSRI and SNRI Risks
SSRIs and SNRIs are widely prescribed for depression and anxiety. While generally considered safe, some studies have suggested a potential link between these medications and an increased risk of heart attacks, particularly in individuals with pre-existing heart disease or risk factors.
Consulting with Healthcare Providers
For individuals with heart disease or risk factors, it is important to discuss the potential cardiovascular risks of antidepressants with healthcare providers. They can help determine the most appropriate medication and dosage to balance mental health needs with heart health concerns.
Can Antibiotics Cause Heart Attacks?
Antibiotics are essential for treating bacterial infections, but some have been linked to cardiovascular side effects, including an increased risk of heart attacks. Understanding which antibiotics pose the greatest risk and how to use them safely is crucial for protecting heart health.
Fluoroquinolones and Heart Risk
Fluoroquinolones, a class of antibiotics, have been associated with cardiovascular side effects, including heart rhythm abnormalities and an increased risk of heart attacks. Examples of fluoroquinolones include ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin.
Safe Use of Antibiotics
To minimize the risk of heart issues when using antibiotics:
- Use antibiotics only when necessary and prescribed by a healthcare provider
- Discuss any existing heart conditions or risk factors with the prescribing doctor
- Follow the prescribed dosage and duration of treatment
- Report any unusual symptoms or side effects to a healthcare provider
Alternative Treatments
In some cases, alternative antibiotics or treatment options may be available for individuals with heart disease or risk factors. Healthcare providers can help determine the most appropriate course of treatment to effectively manage infections while minimizing cardiovascular risks.
Medications for Chronic Conditions and Heart Risk
Individuals with chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and asthma often require long-term medication management. While these medications are essential for controlling symptoms and preventing complications, some may also pose risks to heart health.
Diabetes Medications
Medications used to manage diabetes, such as certain oral hypoglycemic agents, have been associated with cardiovascular side effects. It is important for individuals with diabetes to work closely with healthcare providers to monitor heart health and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Hypertension Medications
While medications used to treat high blood pressure generally improve heart health, some may have adverse effects. For example, certain beta-blockers and diuretics can affect heart rate and blood volume, potentially impacting heart health.
Asthma Medications
Some asthma medications, particularly certain bronchodilators and corticosteroids, can affect heart rate and blood pressure. Individuals with asthma and heart disease should work with healthcare providers to find the most appropriate treatment plan that balances respiratory and cardiovascular health needs.
Stimulants and Their Effect on Heart Health
Stimulants are medications used to treat conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. While effective for managing symptoms, stimulants can also affect heart health by increasing heart rate and blood pressure.
Common Stimulants
Commonly prescribed stimulants include:
- Adderall (amphetamine/dextroamphetamine)
- Ritalin (methylphenidate)
- Concerta (methylphenidate)
- Vyvanse (lisdexamfetamine)
Cardiovascular Risks
Stimulants can increase heart rate and blood pressure, which may pose risks for individuals with pre-existing heart conditions or risk factors. It is important to monitor heart health and discuss any concerns with healthcare providers when taking stimulants.
Safe Use of Stimulants
To minimize cardiovascular risks when using stimulants:
- Discuss any existing heart conditions or risk factors with healthcare providers
- Follow the prescribed dosage and duration of treatment
- Regularly monitor heart rate and blood pressure
- Report any unusual symptoms or side effects to a healthcare provider
Are There Safe Alternatives?
For individuals concerned about the cardiovascular risks associated with certain medications, exploring safe alternatives is an important step in protecting heart health. Safe alternatives may include different medications, lifestyle changes, or alternative therapies.
Alternative Medications
In some cases, alternative medications with a lower risk of cardiovascular side effects may be available. Healthcare providers can help determine the most appropriate alternative treatment options based on individual health needs and risk factors.
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk of heart attacks and improve overall cardiovascular health. Key lifestyle changes include:
- Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga
Alternative Therapies
In some cases, alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage, or herbal supplements may provide relief from symptoms without the cardiovascular risks associated with certain medications. It is important to discuss any alternative therapies with healthcare providers to ensure their safety and effectiveness.
Recognizing Warning Signs
Being aware of the warning signs of a heart attack or adverse medication effects on the heart is crucial for prompt intervention and treatment. Recognizing these signs early can help prevent serious complications and improve outcomes.
Heart Attack Warning Signs
Common warning signs of a heart attack include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Pain in the arms, neck, jaw, or back
- Shortness of breath
- Cold sweat
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
Adverse Medication Effects
In addition to heart attack symptoms, individuals taking medications with potential cardiovascular risks should be aware of other warning signs, such as:
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Swelling in the legs or ankles
- Unexplained weight gain
- Persistent fatigue or weakness
When to Seek Medical Help
If any warning signs or symptoms are experienced, it is important to seek medical help immediately. Early intervention can prevent serious complications and improve outcomes.
How to Talk to Your Doctor About Medication Risks?
Open communication with healthcare providers is essential for managing medication risks and protecting heart health. Discussing concerns and asking questions can help ensure that treatment plans are safe and effective.
Preparing for the Conversation
Before discussing medication risks with healthcare providers, it can be helpful to:
- Make a list of all current medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements
- Note any concerns or questions about medication risks
- Gather any relevant medical history or information about heart health
Questions to Ask
When discussing medication risks with healthcare providers, consider asking questions such as:
- What are the potential cardiovascular risks of this medication?
- Are there safer alternatives available?
- How can I monitor my heart health while taking this medication?
- What lifestyle changes can I make to reduce heart attack risk?
Follow-up and Monitoring
After discussing medication risks, it is important to follow up with healthcare providers regularly to monitor heart health and adjust treatment plans as needed. Regular communication can help ensure that treatment plans remain safe and effective.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Heart Attack Risk
In addition to managing medication risks, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk of heart attacks and improve overall cardiovascular health. Key lifestyle changes include:
Heart-Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help lower cholesterol levels, reduce blood pressure, and improve heart health. Limiting processed foods, saturated fats, and added sugars can also contribute to a heart-healthy diet.
Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling, can help improve cardiovascular fitness, lower blood pressure, and reduce the risk of heart attacks. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Smoking Cessation and Alcohol Moderation
Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption can significantly reduce the risk of heart attacks. Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of plaque buildup, while excessive alcohol consumption can raise blood pressure and contribute to heart disease.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can negatively impact heart health by increasing blood pressure and contributing to unhealthy behaviors such as overeating or smoking. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing, can help improve heart health and overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What should I do if I experience heart attack symptoms while taking medication?
If you experience heart attack symptoms while taking medication, seek medical help immediately. Early intervention can prevent serious complications and improve outcomes.
2. Can I stop taking my medication if I'm concerned about heart attack risk?
Do not stop taking medication without consulting with your healthcare provider. They can help determine the best course of action to balance medication benefits with potential risks.
3. Are there any dietary supplements that can help protect heart health?
Some dietary supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids, Coenzyme Q10, and magnesium, may support heart health. However, it is important to discuss any supplements with healthcare providers to ensure their safety and effectiveness.
4. How can I monitor my heart health while taking medication?
Regularly monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, heart rate, and weight. Report any unusual symptoms or changes to your healthcare provider promptly.
5. Can lifestyle changes alone reduce the risk of heart attacks?
While lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of heart attacks, they should be part of a comprehensive approach that includes proper medical management and monitoring. Consult with healthcare providers to develop a personalized plan.
6. What should I do if I have concerns about medication interactions?
Discuss any concerns about medication interactions with your healthcare provider. They can review your medications and recommend any necessary adjustments to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Conclusion
Understanding the potential risks of medications that may cause heart attacks is crucial for making informed decisions about healthcare. By being aware of the medications with potential cardiovascular risks, recognizing warning signs, and adopting heart-healthy lifestyle changes, individuals can protect their heart health and reduce the risk of heart attacks. Open communication with healthcare providers is essential for managing medication risks and ensuring safe and effective treatment plans. By taking proactive steps to protect heart health, individuals can enjoy a healthier, more fulfilling life.
You Might Also Like
Democrat Strategist: Trump May Surprise - An In-Depth AnalysisDodgers DFA Former Top Prospect: A Comprehensive Analysis
McCaffrey's Reaction To Skattebo's Jersey: A Tale Of Inspiration And Legacy
Jean-Pierre's Stance On Trump's Flag Critique: A Formal Response
Insights And Reactions: Tarlov, Pirro Clash On Fake Claim
Article Recommendations
- Todd Lerfondler A Comprehensive Look At His Life Achievements And Legacy
- The Extraordinary Career Of Fred Gwynne Legendary Actor
- When Was Marlon Jackson Born Heres His Date Of Birth